The Brady iOS SDK Demo
XCode Prerequisites
Software Requirements
To use the Brady SDK, you must have at least:
- iOS 15 or higher
- Swift 5
Add the SDK to your XCode Project
To use the iOS SDK Framework, follow the steps below.
- Download the iOS SDK from bradyid.com.
- Create a new Xcode Application
-
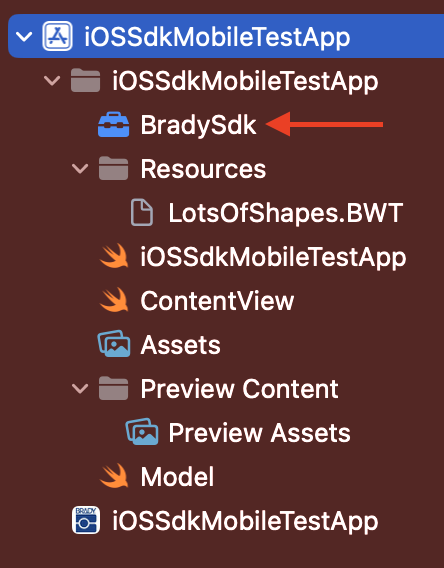
After unzipping the "BradySdk-iOS.zip", drag and drop the ".xcframework" file to the root of your app in the file tree.
-
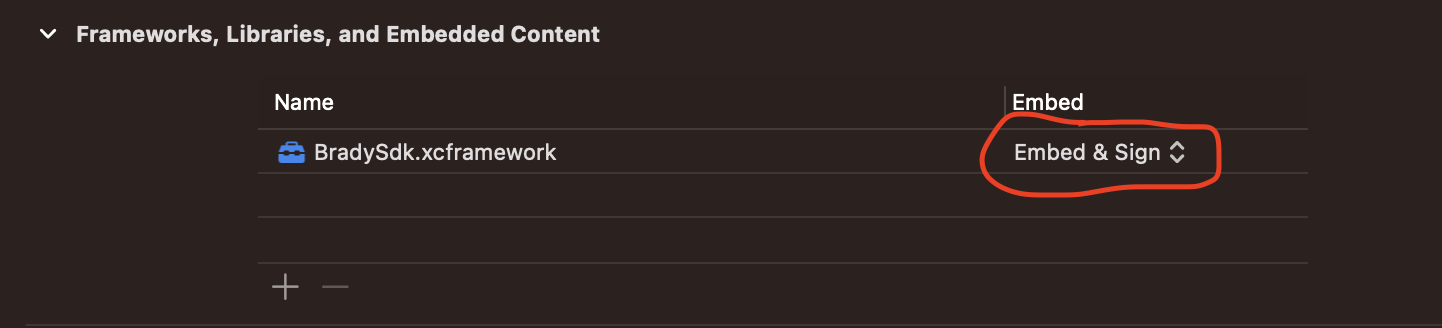
Xcode will now show the framework under the "Frameworks, Libraries, and Embedded Content" section in the App Target.
-
Change the Embedded field to "Embed & Sign."
-
Test that everything is added correctly by typing "import BradySdk" at the top of any file in your app (it will autofill the name if it can find the framework).
Adding Permissions
In order to use Bluetooth and Wi-Fi discovery and connection within the SDK, you must let the user allow these permissions the first time the application is opened. This pop-up will appear automatically when these permissions are added to the "info.plist" in your app.
-
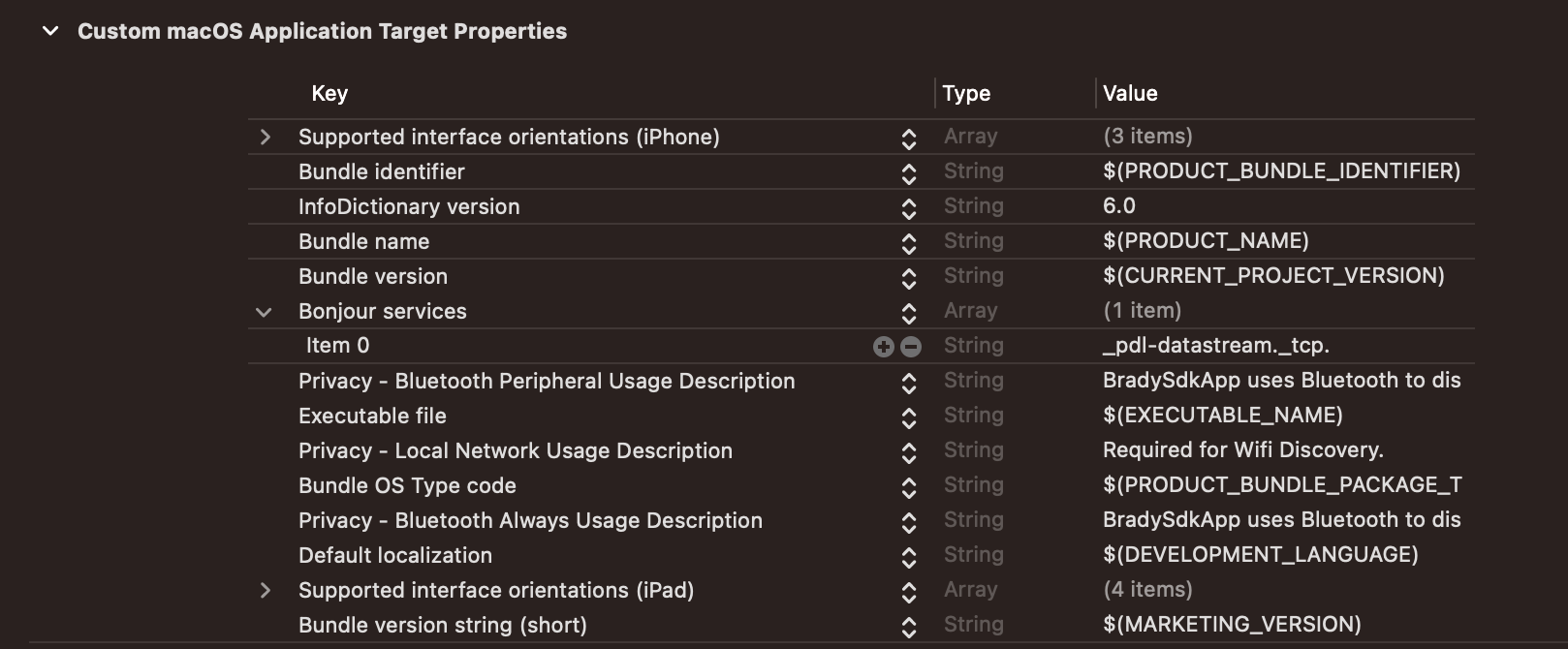
Under the "Info" tab off your app settings, add the following permissions underneath "Custom Target Properties."
- Privacy - Bluetooth Always Usage Description
- Privacy - Bluetooth Peripheral Usage Description
- Privacy - Local Network Usage Description
- Bonjour services:
- Enter the value "_pdl-datastream._tcp." for the Key "Item 0".
- You may enter whatever message you would like under the value column for these permissions (excluding Bonjour Services).
- To verify this worked, run your application and you will see a "pop up" window asking you to allow the permissions.
- If a user cancels the pop up and selects "Don't Allow", they can always allow these permissions in their device's "Settings" application.
Versions >=1.7.0
Custom Brady fonts are no longer embedded in the iOS SDK. Therefore, they must be downloaded here.
The custom Brady fonts only need to be downloaded and embedded into your application if the BWT files being used by your application were designed with any of these fonts. To embed them in your iOS application:
- Create a folder named "fonts" in your application's "Resource" directory.
- Add the desired fonts to this new folder.
- Drag and drop each font to the "Copy Bundle Resources" section to add the fonts to the main bundle of your application.
- In XCode click your application's .xcodeproj file >> Build Phases Tab >> Expand the Copy Bundle Resources dropdown >> this is where you drag and drop the fonts.
Printer Discovery
Before starting this tutorial, it is important to note that the SDK was not designed to discover, connect, print, and disconnect all at once. The printer itself will still struggle to receive and send data this quickly.
Example: It is not recommended to design an app with a single button labeled "Print" where the app would discover, connect, print, and then disconnect on the button click.
Requesting Permissions
In order to discover nearby printers, the user must approve the required permissions:
(Reference the Setup page for the iOS SDK)
- This should prompt the user only on the initial opening of the application.
- If the user does not allow permissions when prompted, they can always go into the settings app to allow them later. However, the user will never be able to discover printers without approving these permissions.
Implementing Discovery
- Create a new PrinterDiscovery object:
var printerDiscovery: PrinterDiscovery = PrinterDiscoveryFactory.getPrinterDiscovery(listeners: [PrinterDiscoveryListener])
- Start discovering nearby printers:
- PrinterDiscoveryListener must be implemented in the UI's class where you will store the discovered printer objects.
- This will force you to add the printerDiscovered method that you can implement like:
- PrinterDiscoveryListener must be implemented in the UI's class where you will store the discovered printer objects.
public func printerDiscovered(discoveredPrinterInformation: DiscoveredPrinterInformation) {
if(!foundPrinters.contains(where: {discoveredPrinterInformation.getName() == $0.getName()})) {
foundPrinters.append(discoveredPrinterInformation)
}
}
-
To start discovering Bluetooth Low Energy devices, call:
printerDiscovery.startBlePrinterDiscovery()printerDiscovery.startWifiPrinterDiscovery()
-
To stop the discovery scan for Bluetooth Low Energy devices, call:
printerDiscovery.stopPrinterDiscovery()
-
To find the most recent printer you successfully connected to, call:
let lastConnectedPrinter = printerDiscovery.getLastConnectedPrinterName()
Displaying Printers
Swift has specific tags that allow a list to automatically notify the UI if it has changed. These tags are called @Published and @ObservedObject.
In order for the UI to update immediately when a new printer is found, initialize the foundPrinters list as such:
@Published private var foundPrinters = [DiscoveredPrinterInformation]()
In order for our "Model" class to comply, we need to inherit ObservableObject. Your "Model" class header may look like this after fully implementing the Brady SDK:
public class Model: PrinterUpdateListener, PrinterDiscoveryListener, ObservableObject {
Lastly, initialize the "Model" object in the UI class. Initialize it as such:
@ObservedObject var model = Model()
Now, whenever we call a method on the variable "model", it will send the UI its updated state.
To summarize, now a user could initialize a NavigationView holding a list of items in their UI. In this case, the list will represent printer names. With this implemented, the UI will update whenever a new printer is found and the list of printers in our "Model" class is changed.
Printer Connection
Connecting to a Printer
- The connectToDiscoveredPrinter method uses the intialized PrinterDiscovery object and attempts to connect to the desired printer and returns a PrinterDetails object.
printerDetails = try await printerDiscovery.connectToDiscoveredPrinter(printerSelected: printerToConnectTo!, listeners: listeners)
printerSelectedis the DiscoveredPrinterInformation object which represents the printer that will be connected.List<PrinterUpdateListener>is a list of listener objects. (This works similar to a "Context" object because we can initialize it by adding "self" to a list.)
Example:
var listeners: Array<PrinterUpdateListener> = []
listeners.append(self)
//Iterate through all found printers.
var printerToConnectTo: DiscoveredPrinterInformation? = nil
for printer in foundPrinters {
//If the user-selected printer name matches one of the found printer's,
//set this printer object as the one we want to connect to.
if printer.getName() == printerSelected {
printerToConnectTo = printer
//Stop the scan since we found the printer we want to connect to.
printerDiscovery.stopPrinterDiscovery()
}
}
//Connect to the found printer.
printerDetails = try await printerDiscovery.connectToDiscoveredPrinter(printerSelected: printerToConnectTo!, listeners: listeners)
- After the connection has successfully finished, it will return a PrinterDetails object populated with details about the printer, such as name and model number, battery life, and installed part/supply information.
- If the connection has failed, it will return nil.
- After the connection is finished, the PrinterDetail's haveOwernship() method can also be used.
- This method will return a Boolean representing the ownership of the desired printer to the used mobile device. (Reference the "PrinterDetails" page under "Printer Connection" for more details.)
Automatic Connection
Once your application has connected to a printer for the first time, it will store the printer object internally. In the future, you can add a feature to your app that grabs this object and connects to it automatically without the user manually selecting a printer from the UI:
//Use this PrinterDiscovery method to find the name of the printer available to automatically connect to.
lastConnectedPrinterName = printerDiscovery.getLastConnectedPrinterName()
//Now, whenever a printer is discovered, it'll compare it immediately to this printer name.
//If it matches, it'll attempt to connect right away when the app starts.
if newlyDiscoveredPrinter == model.lastConnectedPrinterName {
connected = try await model.connectToDiscoveredPrinter(printerSelected: printerToConnectTo!, listeners: listeners)
}
Calling printerDetails.disconnect() will make the app "forget" the current printer internally and will not connect to it automatically afterwards. Alternatively, calling printerDetails.disconnectWithoutForget() will disconnect from the printer temporarily, but getLastConnectedPrinterName() will still return the name of the printer you just disconnected from.
OWNERSHIP NOTE: Using an M211 introduces the concept of "ownership". When connecting to an M211 with a mobile device for the first time, the blue light on the M211 should be blinking. If the light is solid blue, another mobile device "owns" the printer and only that device will be able to connect. In the event that a connection fails, a device can still have "ownership". Therefore, being connected and having ownership are not synonymous. To connect using a different mobile device, hold the power button for five seconds to release ownership.
Disconnecting from Printers
- Simply call
try await printerDetails?.disconnect() - After disconnecting, it is recommended to start discovering for printers again.
Performing Other Printer Operations
-
Feed a label:
let result = try await printerDetails?.feedSupply()
-
Cut a label:
let result = try await printerDetails?.cutSupply()
-
Set the printer's automatic shutoff timer:
let result = try await printerDetails?.setAutomaticShutoffTime(timeInMinutes: Int)
Connect/Disconnect Permutations
Scenario #1: If you connect for the first time and the printer disconnects unexpectedly (turned off, taken out of range, etc.), the printer will send a "CurrentStatus" update to the PrinterUpdate override method.
- Because of this scenario, you must have a way to notify your UI view that the printer is no longer connected.
override public PrinterUpdate(list: List<PrinterProperties>) {
for property: PrinterProperties in list {
if property == PrinterProperties.CurrentStatus {
if printerDetails.getPrinterStatusMessage() == "PrinterStatus_Disconnected" {
//ENTER CODE HERE TO HANDLE THE DISCONNECT (start discovery again or disable the print button for example)
}
}
}
}
Scenario #2: You must only use reconnect() if you have previously connected since the app has been opened. If you connect for the first time, close the app, open the app, and call reconnect(), it will not work because the PrinterDetails will once again be nil.
- Because of this scenario, you must only use the reconnect() method if the printer has disconnected for an unknown reason and you are attempting to reconnect.
if printerDetails != null {
printerDiscovery.connectToDiscoveredPrinter(context, printerSelected, listener);
}
else {
printerDetails.reconnect()
}
Scenario #3: You call printerDetails.disconnect() to forget the connected printer. This "forgets" the printer internally. Therefore, reconnect() will not work until you connect with connectToDiscoveredPrinter and are successful again. Calling printerDetails.disconnect() also releases ownership (if you are using an M211) so the blue blinking light is a clear indication that you are properly disconnected. However if you call printerDetails.disconnectWithoutForget(), the previously connected printer will be remembered still. Therefore, this is a perfect situation to use reconnect().
Open Templates
Before adding code, create a subdirectory within your app's root directory to place template files (.BWT).
Initialize a Template Object
- Create a dropdown menu on the UI to allow users to select a template.
Menu {
Picker("Template Picker", selection: $selection) {
//Adding the template name strings will go here.
}
} label: {Text(selection).font(.caption)}
- Populate the dropdown menu with the available file names.
Menu {
Picker("Template Picker", selection: $selection) {
//*NEW*
let templateList: [String] = [--INSERT NAMES OF AVAILABLE TEMPLATES--]
ForEach(templateList, id: \.self) {
Text($0).font(.footnote)
}
}
} label: {Text(selection).font(.caption)}
- Open the resource as an InputStream for when the user selects a template from the dropdown menu,
public func getSelectedTemplate(context: AppContext, selection: String) -> Template? {
do{
//For this line to work, you MUST have a subdirectory at your projects root.
//Otherwise, it will not be able to find the fileReferenceLiteralResourceName.
let filePath = URL(fileReferenceLiteralResourceName: selection)
let templateData: Data = try Data(contentsOf: filePath)
let iStream: InputStream = InputStream(data: templateData)
}
catch let error {
print(error)
}
return nil
}
- Call the SDK's getTemplate() method to retrieve the Template object
public func getSelectedTemplate(context: AppContext, selection: String) -> Template? {
do{
//For this line to work, you MUST have a subdirectory at your projects root.
//Otherwise, it will not be able to find the fileReferenceLiteralResourceName.
let filePath = URL(fileReferenceLiteralResourceName: selection)
let templateData: Data = try Data(contentsOf: filePath)
let iStream: InputStream = InputStream(data: templateData)
//*NEW*
return TemplateFactory.getTemplate(template: iStream)
}
catch let error {
print(error)
}
return nil
}
- After successfully initializing the Template object, iterate through its placeholders to set any desired values. (Example: An EditText view to allow a user to set the value of a specific field in the template.)
Setting a Placeholder Value
After a successful initialization of a template object, the getTemplateData() method can be used to set a specific value to a placeholder on the template. In this example, iterate through all template data until we find a placeholder with the name of "ExamplePlaceholder" and we change it to say "Example."
for placeholder in try template?.getTemplateData() {
if placeholder.getName() == "ExamplePlaceholder" {
placeholder.setValue(value: "Example")
}
}
If you would like to display to your user what type of object the current placeholder is, use the following code to retrieve a TemplateObjectType. This enumeration represents the type of object/placeholder. This is useful if a template placeholder was renamed in BWS that doesn't represent the type of object very well. For example a barcode in BWS could be renamed to "ExamplePlaceholder" in BWS. Your user would have no idea that this object is a barcode without TemplateObjectData.getTemplateObjectType().
for placeholder in try template?.getTemplateData() {
if placeholder.getName() == "ExamplePlaceholder" {
//This can return the values StaticText, Text, Rectangle, Barcode, Image, PolyPolyLine, or Other
let placeholderType = placeholder.getTemplateObjectType()
}
}
Preview the Template
- Call template.getPreview(labelNumber, dpi, maxPixelWidthAndHeight)
(Reference the Template page).
func templatePreview(selection: String) -> some View {
do{
//Where "template" is the Template object you found earlier.
let bitmap: CGImage? = try template?.getPreview(labelNumber: 1, dpi: 96, maxPixelWidthAndHeight: 200)
if bitmap == nil {
return Image(uiImage: UIImage())
}
return Image(uiImage: UIImage(cgImage: bitmap!)).resizable()
}
catch let error {
print(error)
}
return Image("ERROR")
}
Printing
- To print, call:
let printingStatus: PrintingStatus = try await (printerDetails?.print(template: template!, printingOptions: printingOptions, dontPrintTrailerFlag: true)) ?? PrintingStatus.PrintingFailed)
templateis the Template object (reference the Open Templates page).printingOptionsis the PrintOptions object we initialize (reference below).dontPrintTrailerFlagis a Boolean that represents if we want a trailer on our label.
The SDKs PrintingOptions is used to set CutOptions and the number of copies to print, like:
let printingOptions: PrintingOptions = PrintingOptions()
printingOptions.cutOption = CutOption.EndOfJob
printingOptions.numberOfCopies = 1
printingOptions.isCollated = true
-
Because the print() method is asynchronous, the await keyword is used. This also allows this method to return the result of the print operation after it is finished in the form of a PrintingStatus object.
-
Check the status of the print job like this:
if printingStatus == PrintingStatus.PrintingSucceeded {
print("Print Successful!")
}
else {
print("Print Failed!")
}
- Alternatively, if the desire is to simply print an image instead of a Brady Workstation template, you may use the print method shown below.
public func printImage(image: UIImage) async {
let printingOptions: PrintingOptions = PrintingOptions()
printingOptions.cutOption = CutOption.EndOfJob
printingOptions.numberOfCopies = 1
do {
let printingStatus: PrintingStatus = try await (printerDetails?.print(image: image, printingOptions: printingOptions, dontPrintTrailerFlag: false)) ?? PrintingStatus.PrintingFailed
if printingStatus == PrintingStatus.PrintingSucceeded {
debugPrint(" Please wait...")
}
else {
debugPrint("Print Failed!")
}
}
catch let error as SdkApiException {
debugPrint("Printing Error...")
}
}
- To convert a PNG, JPG, JPEG, WEBP, or SVG file to a UIImage, simply do:
//The PNG file "bradylogo.png" was selected by a user.
let selection: String = "bradylogo.png"
let imageToLoad = UIImage(named: selection) ?? UIImage()